Abstract
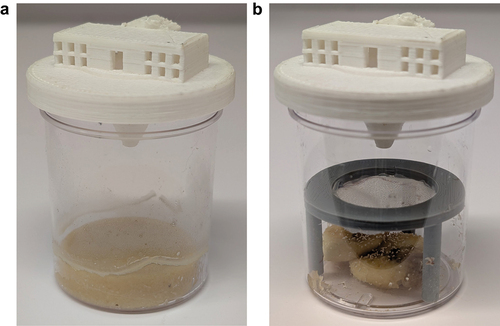
Drosophila melanogaster, the common fruit fly, has been instrumental to our understanding of evolution, genetics and disease. There are benefits to studying these flies in the wild, including assessment of their naturally occurring microbiota. To facilitate efforts to catch wild D. melanogaster, we designed two fly traps and evaluated several candidate attractants. The first trap utilized a stable food substrate that can be used to catch live flies to establish new lab colonies. The second trap was designed to be reusable and easy to ship to enable the collection of flies over time from diverse locations. We evaluated several chemical attractants derived from banana and from marula fruit, which is the proposed ancestral food host of D. melanogaster. We found that wild flies were preferentially attracted to banana-based odorants over marula-derived ones. Overall, these traps and attractants represent an inexpensive and simple option for the collection of wild D. melanogaster and related species for sampling or colony establishment.